Our body obtains nutrients through the food we eat. Nutrients are substances that serve as energy sources or form the structural components of our body. The three major nutrients are carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, which are three major organic compounds primarily composed of carbon and involved in chemical reactions. These three nutrients are essential building blocks for the body. In addition to these three, minerals (inorganic substances), vitamins, and water are added to make up the six major nutrients.
Carbohydrates are broken down and transformed during the digestion process after consumption. They primarily provide energy to the cells in the form of glucose, a simple sugar. Carbohydrates serve as an energy source for various tissues, such as the brain, nerves, lungs, and muscles. They are also stored in the liver and muscles in the form of glycogen, which is made up of multiple glucose molecules. In addition to being an energy source, carbohydrates also play a crucial role in various cellular processes, such as activating proteins by interacting with other substances in the body, including proteins and lipids. Carbohydrates are also an essential component of nucleic acids, which make up DNA and RNA.
After being consumed, proteins are broken down into amino acids during the digestion process. Amino acids are then used as building blocks for synthesizing essential proteins in the body. These proteins play crucial roles in various metabolic processes, immune functions, signal transmission, and almost all life activities. Our body considers proteins as essential components, forming the basic units of cells and being involved in diverse functions. It’s like the human body is a “society composed of various proteins,” which emphasizes the vital role of proteins in life. Proteins are the major components of muscles, hair, nails, and many other essential parts of our body.
Fats are often thought to be harmful to diets, but they have functions beyond just storing energy. They are also used for structural purposes, such as being a primary component of cell membranes. In addition, fats play an active role in metabolic functions within the human body.
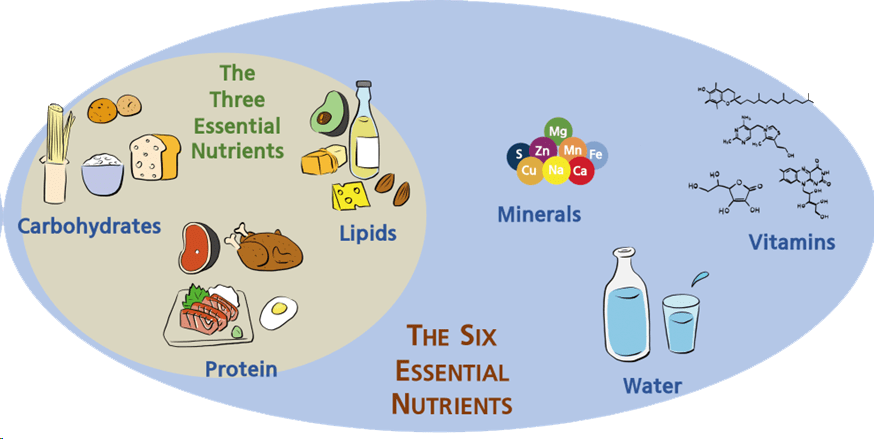
Minerals, comprising the 6 essential nutrients, exist in very small amounts within our body. These minerals are inorganic and are necessary for our body’s proper functioning. Some of the essential minerals include iron, calcium, phosphorus, sodium, copper, zinc, chlorine, and iodine. On the other hand, vitamins are organic molecules that are also important for our body’s proper functioning. Although we do not need vitamins in large quantities, we cannot produce them ourselves, so we must consume them through food.
Water is the source of life. All forms of life originated from water, and it still plays a vital role in creating life today. Since more than 70% of our bodies are composed of water, all the phenomena that occur in our bodies happen in water. The unique physical and chemical properties of water distinguish it from other solvents. In chemistry and life sciences, water is considered an essential substance in all phenomena in the world, including life phenomena, to such an extent that all substances in the world can be primarily classified as “water-soluble” or “water-insoluble.” Some people even refer to water as one of the 5 major nutrients, even though it is not technically a nutrient, as it forms the basis of life.
References
1. https://www.who.int/elena/nutrient
3. Campbell et al. (2017) Essential biology, 11th Ed., Pearson Education, In

Leave a comment